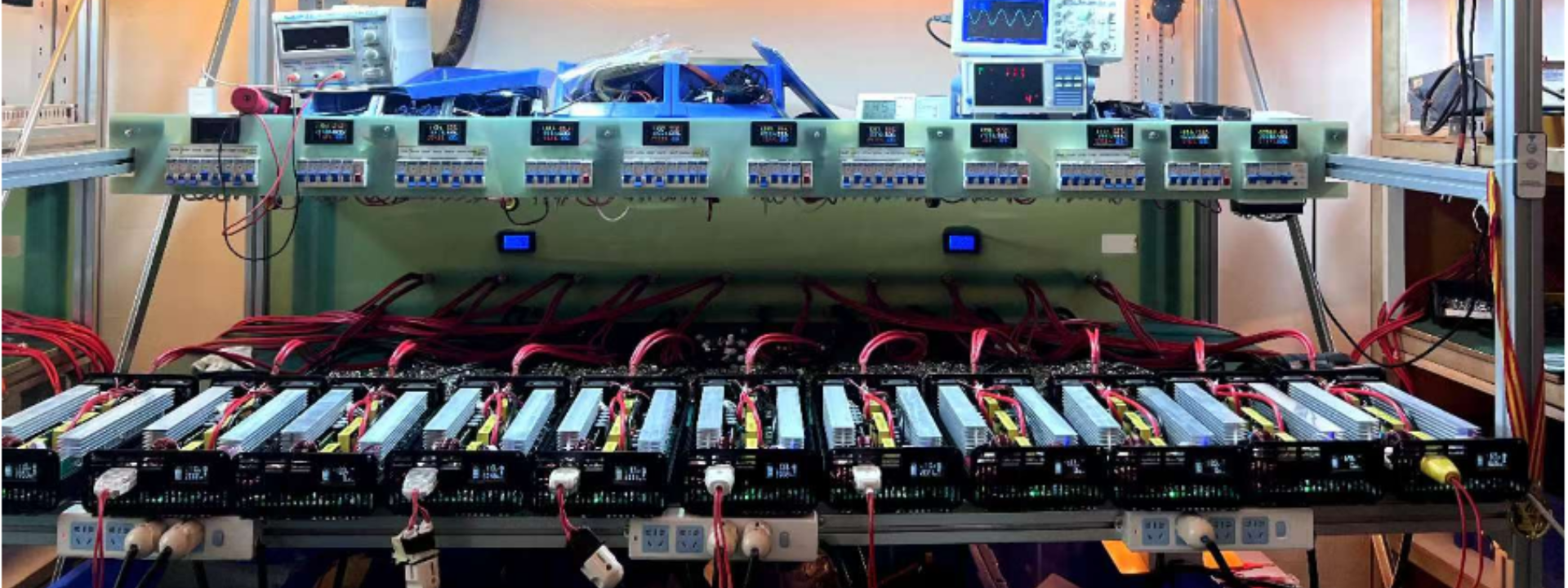
An inverter is a device that converts direct current into alternating current. Its main function is to convert the electrical energy generated by a DC power source such as a solar panel, wind power generator or power battery into alternating current for home, commercial or industrial use. Inverters are widely used in many fields such as solar power generation, wind power generation, UPS power supply, electric vehicle charging piles, etc. Inverters can be divided into many different types according to different application requirements. The classification, selection and wiring methods of inverters will be introduced in detail below.
Classification of inverters
Pure sine wave inverter: Pure sine wave inverter can accurately convert direct current into pure sine wave alternating current. Its output electrical waveform has high quality and is suitable for occasions with high requirements for power quality, such as medical equipment, precision instruments, etc.
Modify sine wave inverter: Modify sine wave inverter can convert direct current into alternating current that is close to a sine wave. Its output electrical waveform quality is relatively low, but it can meet the needs of most household electricity and general electrical equipment.
Square wave inverter: Square wave inverter converts direct current into square wave alternating current. Its output electrical waveform quality is low, and the waveform has large distortion. It is suitable for some applications that do not require high power quality, such as power tools, lighting equipment, etc.
Bridge inverter: The bridge inverter uses a bridge structure composed of four switching tubes to convert DC power into AC power. The bridge inverter has the characteristics of large output current and high output power, and is suitable for high-power applications, such as electric vehicle charging piles, industrial equipment, etc.
Inverter selection
When selecting an inverter, the following factors need to be considered:
Output power: Determine the output power of the inverter according to demand. Generally, the rated output power of the inverter should be greater than or equal to the power of the required electrical equipment.
Output waveform: Determine the output waveform of the inverter according to demand. If the power quality requirements are high, it is recommended to choose a pure sine wave inverter; if the power quality requirements are low or it is used for general household appliances, you can choose to modify the sine wave inverter or square wave inverter.
Input voltage: Determine the input voltage range of the inverter to match the voltage output of a DC power source such as a battery or solar panel.
Rated current: Determine the rated current of the inverter according to the demand. Generally, the rated current of the inverter should match the rated current of the required electrical equipment.
Inverter efficiency: Consider the conversion efficiency of the inverter. High-efficiency inverters can better utilize electrical energy, reduce energy loss, and improve the overall performance of the system.
Protection function of the inverter: Select an inverter with overvoltage, overload, overtemperature and other protection functions to provide better stability and safety.
Wiring method of the inverter
The wiring method of the inverter may vary depending on the specific inverter model and application scenario, but generally follows the following principles:
DC input terminal wiring: Connect the positive and negative poles of the DC power supply (such as solar panels, power batteries, etc.) to the positive and negative poles of the inverter respectively. Ensure that the wiring is firm and reliable, and pay attention to waterproof measures.
AC output terminal wiring: Connect the AC output terminal of the inverter to the user demand side (such as home power grid, electrical equipment, etc.). A standard three-core cable is usually used for wiring, with one conductor connected to the AC output terminal of the inverter, and the other two conductors connected to the L (cable) and N (neutral) terminals of the AC power line at the user's demand end.
Grounding: The inverter should be grounded to improve safety and system stability. Usually, the metal casing of the inverter needs to be grounded, and the metal casing of the inverter can be connected to the ground wire through the grounding wire.
It should be noted that the above is a general introduction to the inverter wiring method, and the specific operation should be carried out according to the specific model and manual of the inverter. Before wiring, make sure that the power switch of the DC power supply has been disconnected, and be careful during the wiring process to avoid electric shock or other accidents.
Summary
The inverter is a device that converts DC power into AC power. According to different application requirements, it can be divided into pure sine wave inverters, modified sine wave inverters, square wave inverters, bridge inverters and other types. When selecting an inverter, factors such as output power, output waveform, input voltage, rated current, inverter efficiency and protection functions need to be considered. The wiring method of the inverter generally includes the wiring of the DC input terminal, the wiring of the AC output terminal and the grounding of the inverter.