In the universe, the space shuttle is an important carrier for human exploration of space, and its power system is the "lifeline" that maintains the operation of all key equipment. From cabin lighting to computer control, from life support to scientific experiments, a stable and reliable power supply is directly related to the success of the mission and the safety of astronauts.
About the aircraft power system
1. Composition of the aircraft power system
① Main power supply: a system directly or indirectly transmitted by the engine; it is the energy source for all equipment on board.
② Auxiliary power supply: working conditions: when the aircraft is on the ground and the main power supply is not working; or as a backup power supply for the main power supply in the air. Type: aviation battery, APU.G. Function: pre-flight/post-flight preparation (working on the ground), starting the main engine, etc., it can replace the failed main generator in the air to supply power to the aircraft.
③ Secondary power supply: convert the main power supply power into another form or specification of power to meet the needs of different power-consuming equipment.
④ Emergency power supply: enabled when the main power supply and auxiliary power supply all fail during flight, and can only supply power to important power-consuming equipment (critical loads) on the aircraft. Aviation battery (BAT), static inverter (INV) ram air turbine generator (RAT), hydraulic motor driven generator (HMG)
⑤ Ground power supply: powered by an external power supply when performing ground inspections at the airport or starting aircraft engines. At this time, the main power supply does not supply power.
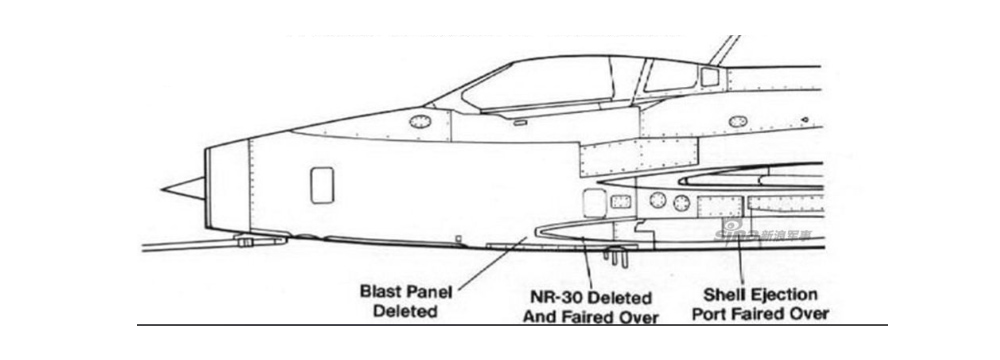
2. Main types and characteristics of aircraft power systems
① Low-voltage DC power supply (28V) Secondary power supply: rotary converter, static converter; Emergency power supply: aviation battery.
② VSVF: Features: No CSD required, directly transmitted by the aircraft engine, simple structure, light weight, high reliability. Easy to form a starting power generation system. The near constant frequency of turboprop aircraft is a narrow variable frequency AC power supply system. Turbojet aircraft need to be equipped with a frequency converter, which is a wide variable frequency AC power supply system.
③ CSCF: Transmitted by the aircraft engine through a constant CSD, currently the most commonly used form for large jet aircraft.
④ VSCF: No CSD, high reliability, low life cycle cost; but the technology is unstable. VSCF power supply and CSCF power supply are interchangeable, no need to change the power distribution and power consumption parts, strong versatility.
⑤ 270V high-voltage DC power supply: used for military aircraft.
3. Classification of aircraft electrical loads:
According to the purpose, they are divided into electric mechanism (30%), heating and anti-icing load (40%), avionics equipment (20%), lighting equipment (8%). According to the importance, key equipment or the most important equipment (affecting the flight safety of the aircraft) usually adopts 4 redundant power supply, that is, two independent main power supplies, one backup power supply, and one emergency power supply. Important equipment (about 50% affecting the safety of aircraft personnel) usually adopts 3 redundant power supply, that is, two main power supplies and one backup power supply. General equipment and kitchen equipment (kitchen heating accounts for about 40%) are unloaded objects during single-engine flight or starting the main engine.
4. Power supply mode:
Multi-power DC power supply system generally adopts parallel power supply mode, and multi-power constant frequency AC power supply system has two power supply modes: single power supply and parallel power supply.
5. Aircraft power grid structure and characteristics:
DC power grid: single-wire system, with the fuselage as the negative line.
AC power grid:
A three-phase four/three-wire system with the fuselage as the neutral line. There are two voltage specifications: phase voltage 115V and line voltage 200V, which are safer.
B Three-phase three-wire system without neutral line. The load can only be connected to one voltage, line voltage 200V, which is more dangerous in case of failure.
6. Main parameters of constant frequency AC power supply system:
115V/200V, 400Hz three-phase AC sine wave.
——U: Consideration factors: weight, allowable voltage drop of the power grid, wire strength, personnel safety, insulation strength and other factors.
① The higher the voltage, the lighter the weight of the power grid;
② The thinner the wire, the greater the line voltage drop; the cross-sectional area of the wire is limited by mechanical strength, and there is no benefit from too high voltage;
③ The voltage is too high, the weight of the insulation material increases, and it is difficult to extinguish the arc
④ The safety of personnel is poor.
——f: Consideration factors: weight, size, performance, inheritance, etc. of electromagnetic equipment
① For stationary electromagnetic equipment such as transformers and mutual inductors, increasing the frequency can reduce the volume and weight of the iron core;
② For rotating motors such as generators and motors, there is an optimal frequency value. The frequency of 400Hz is more appropriate.
For rotating motors: when f↑→number of pole pairs↑, iron loss↑→volume weight↑.
——Advantages of three-phase system:
① Three-phase generators are small in size and have high power;
② Three-phase power supply has two voltages, phase and line;
③ Three-phase asynchronous motors are better than single-phase asynchronous motors.
——Sine wave: electromagnetic component loss is small and electromagnetic interference is small.
7. The main disadvantages of low-voltage DC power supply system:
A As the power supply capacity increases, the weight of the low-voltage DC power supply system also increases.
B When flying at high speed, the cooling problem of DC generators is also difficult to solve.
C If the main power supply is a DC power supply, the secondary power supply is a converter/converter: low efficiency, large volume and weight; and the AC power consumption is large (accounting for more than 95%), which increases the number of conversion devices.
8. The main advantages of the aircraft AC power supply system:
A The voltage is increased, which reduces the weight.
B There is no brush and commutator, so there is no brush wear problem; and the oil injection cooling method can be used to meet the requirements of high-altitude and high-speed flight.
C AC power is easy to convert, has no rotating parts, is light in weight, small in size, and high in efficiency.
Classic questions and answers about aircraft power supply systems
8.1.What are the components of the aircraft power supply system?
The aircraft power supply system consists of the main power supply, auxiliary power supply, emergency power supply, secondary power supply and ground power socket.
8.2. What is the main power supply of the aircraft? What is the secondary power supply?
The main power supply refers to the power generation system directly or indirectly driven by the aircraft engine, which is the energy source for all electrical equipment on board. It is divided into two categories: DC and AC, which depends on the type of generator.
The secondary power supply is the power converted from the main power supply into another form or specification to meet the needs of different electrical equipment.
8.3. What are the auxiliary power supplies? When the aircraft is on the ground and the main power supply is not working, what power supply is used?
The auxiliary power supply includes aviation batteries and generators driven by auxiliary power units. When the aircraft is on the ground and the main power supply is not working, the electrical equipment on board is powered by auxiliary power or airport ground power.
8.4. What are the commonly used emergency power supplies? When are they used? Who do they supply power to?
Emergency power supplies include aviation batteries and ram air turbine generators. If all the main power supplies fail during the flight of the aircraft, the emergency power supply will be used for power supply. Due to the small capacity of the emergency power supply, it can only supply power to important electrical equipment on the aircraft to ensure the emergency landing or return of the aircraft.
8.5. What is the secondary power supply? What are the secondary power supplies?
The secondary power supply is the power converted from the main power supply into another form or specification of electrical energy to meet the needs of different electrical equipment.
In the low-voltage DC power supply system, the secondary power supply includes rotary converters, static converters, etc., which can convert 28V low-voltage DC into 115V/400Hz single-phase AC.
In the AC power supply system, the secondary power supply mainly includes transformer rectifiers and transformers (TRU), which can convert three-phase AC into low-voltage DC.
8.6. What are the main types of aircraft power supply systems?
The main types of aircraft power supply systems include low-voltage DC power supply systems, variable speed and variable frequency AC power supply systems, constant speed and constant frequency AC power supply systems, and new variable speed and constant frequency AC power supply systems and high-voltage DC power supply systems.
8.7. What are the characteristics (advantages and disadvantages) of low-voltage DC power supply systems?
Advantages:
It can also serve as a starter generator to reduce the weight of airborne equipment.
Disadvantages:
1) Low voltage and high current, so the generator and feeder are heavy.
2) Poor performance at high altitude. (Because the altitude increases, the air becomes thinner, the brushes and commutators wear more and have a shorter lifespan. As the speed increases, the airflow temperature rises, and the DC generator uses the windward ram airflow to cool, so the heat dissipation is poor.
3) The power conversion equipment (DC-AC) is complex and inefficient.
8.8. Why is the frequency parameter of the aircraft AC power system selected as 400Hz?
The frequency is related to factors such as the weight, size and performance of the electromagnetic components:
1) Factors affecting the weight of electromagnetic equipment:
For transformers/mutual inductors, increasing the frequency can reduce weight (reduce the core volume)
For rotating motors, increasing the frequency can reduce weight. The weight is the smallest at around 400Hz.
2) For switchgear, the AC arc is easy to extinguish at 400Hz.
The space shuttle power system integrates the most cutting-edge energy technology - the collaborative work of solar energy, fuel cells and energy storage batteries, demonstrating how humans can harness energy in extreme environments.
Share our interesting knowledge and stories on social media