Analysis of Niche Heat Dissipation Solutions in the Production of High-Power AC/DC Power Supplies
In the manufacturing of high-power AC/DC power supplies, heat dissipation performance directly determines the product's stability, service life, and operational efficiency. Traditional popular heat dissipation solutions such as air cooling and simple liquid cooling are adopted by most manufacturers due to their wide application and mature technology. However, in high power density and special working conditions (such as confined spaces and extreme temperature environments), these solutions are prone to heat dissipation bottlenecks, excessive noise, or cumbersome installation. This article focuses on three niche yet efficient heat dissipation solutions, exploring their technical principles, application advantages, and implementation key points in depth, to provide differentiated heat dissipation solution references for power supply manufacturers.
Microchannel Phase Change Heat Dissipation Technology: Precisely Breaking Through Local High Temperatures
Microchannel phase change heat dissipation technology has gradually emerged in high-power AC/DC power supply heat dissipation with its efficient local temperature control capability, but it has not yet become a mainstream application. The core principle of this technology is to use a microchannel structure (with a channel diameter usually between 50-200 microns) to expand the heat dissipation area. At the same time, it absorbs a large amount of heat through the phase change process of the working fluid (such as specially formulated cooling liquid and refrigerant) (liquid converting to gas), and then 导出 the heat through the condensation end to form a closed-loop heat dissipation cycle.
In high-power AC/DC power supplies, power devices (such as IGBTs and rectifier bridges) are the main heat sources, and their local temperature is often much higher than the overall temperature of the power supply. Traditional heat dissipation solutions are difficult to achieve precise temperature reduction. The microchannel phase change heat dissipation module can be directly attached to the surface of power devices, quickly conducting heat through the microchannel network. After absorbing heat, the working fluid vaporizes rapidly. When the vapor generated during the phase change flows in the microchannels, it can take away several times more heat than the liquid working fluid. Compared with traditional air cooling, the heat dissipation efficiency of this technology is increased by more than 30%, and no additional fans are required, completely solving the noise problem caused by air cooling.
In the implementation process, attention should be paid to the processing accuracy of the microchannel structure and the matching of working fluid selection. Precision etching or 3D printing technology is used to manufacture the microchannel substrate to ensure that the inner wall of the channel is smooth and free of blockages, which can reduce the flow resistance of the working fluid; the working fluid needs to be selected according to the operating temperature range of the power supply, taking into account low freezing point, high boiling point and good thermal stability, to avoid working fluid deterioration or channel corrosion during long-term operation. At present, this technology has been used in a small number of high-end high-power power supplies for military and industrial use, especially for compact power products with a power density exceeding 200W/cm³.
Heat Pipe-Vapor Chamber Composite Heat Dissipation System: Balancing Global Temperature Distribution
Although heat pipe heat dissipation technology is not entirely new, the composite heat dissipation system combining heat pipes and vapor chambers is still a niche application in high-power AC/DC power supplies. The vapor chamber achieves rapid and uniform heat diffusion through a vacuum cavity and internal capillary structure, while the heat pipe, with its ultra-high thermal conductivity (thermal conductivity up to hundreds of times that of copper), exports the heat conducted by the vapor chamber to the heat dissipation terminal over a long distance. The two cooperate to form a closed-loop heat dissipation of "global temperature equalization + efficient heat conduction".
Compared with traditional single heat pipe heat dissipation, the advantage of the composite system lies in solving the pain point of "strong local heat dissipation and large global temperature difference". The internal structure of high-power AC/DC power supplies is complex, and heat sources are scattered. A single heat pipe is difficult to cover all high-temperature areas, which easily leads to premature aging of some devices due to excessive temperature. The vapor chamber can be used as a "heat equalizer" inside the power supply, attached to the surface of the power supply motherboard or power module, quickly conducting heat from different areas to the heat pipe connection point, and then concentrating and exporting the heat to the power supply shell or external heat dissipation device through a heat dissipation network composed of multiple heat pipes.
The key to this scheme lies in the connection process and layout design of heat pipes and vapor chambers. Using vacuum brazing technology to achieve seamless connection between heat pipes and vapor chambers can reduce contact thermal resistance; in terms of layout, the direction and number of heat pipes need to be optimized according to the distribution of heat sources inside the power supply to ensure the shortest heat conduction path and minimum resistance. In addition, the capillary structure inside the vapor chamber (such as grooved or sintered) needs to be customized according to the power of the power supply. The sintered capillary structure is more suitable for working fluid reflux in high-power scenarios due to its high porosity and strong capillary suction. At present, this composite heat dissipation system has been applied in high-power AC/DC power supplies for new energy vehicle charging piles, effectively solving the temperature balance problem of charging piles during long-term outdoor operation.
Nano Thermal Conductive Coating Assisted Heat Dissipation Scheme: Optimizing Interface Heat Conduction
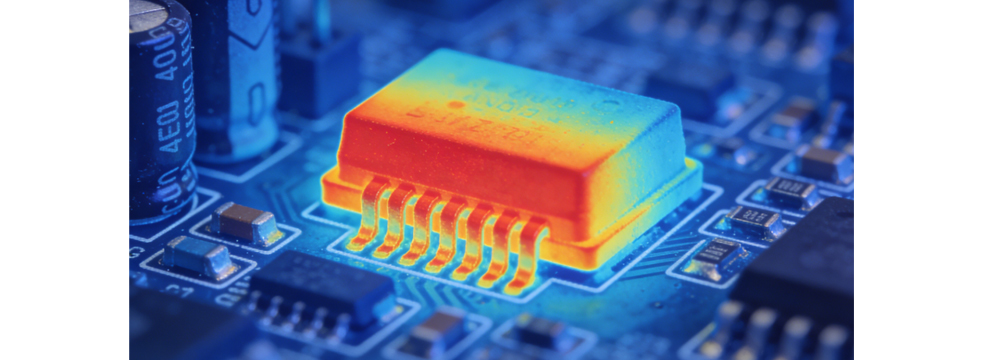
In the heat dissipation of high-power AC/DC power supplies, there are tiny gaps at the contact interface between the heat source and the heat dissipation device. The low thermal conductivity of air will form thermal resistance, affecting heat dissipation efficiency. The nano thermal conductive coating assisted heat dissipation scheme fills the interface gaps by coating special nano materials (such as nano alumina and nano boron nitride composite coatings) on the contact interface, reduces contact thermal resistance, and thus improves the overall heat dissipation effect. Because this scheme needs to be used with other main heat dissipation schemes, it is often ignored by manufacturers and belongs to a niche auxiliary heat dissipation technology.
The heat dissipation principle of nano thermal conductive coatings is based on their unique microstructures and thermal conductivity. The nano-sized particles of the coating material have a large specific surface area. After coating, they can closely fill the gaps between the heat source and the heat dissipation device, eliminating the air interlayer; at the same time, the high thermal conductivity of nano materials (up to 2-3 times that of traditional thermal conductive silicone grease) can accelerate the heat conduction between interfaces and reduce heat accumulation. Compared with traditional thermal conductive silicone grease, nano thermal conductive coatings have better high-temperature resistance (can withstand a temperature range of -50℃ to 200℃), are not easy to age and crack, and no volatile substances are produced, which can maintain stable thermal conductivity for a long time.
In the application of this scheme, it is necessary to control the coating thickness and coating process. If the coating is too thin, it cannot completely fill the gaps; if it is too thick, it will increase thermal resistance. The thickness is usually 50-100 microns; the coating can be applied by spraying, screen printing and other processes to ensure uniform coating and no bubbles. In actual production, nano thermal conductive coatings are often used in combination with microchannel heat dissipation, heat pipe heat dissipation and other schemes. For example, coating nano coatings between power devices and microchannel substrates can reduce interface thermal resistance by more than 40% and further improve the overall heat dissipation efficiency. This scheme is especially suitable for high-power AC/DC power supplies in medical equipment and industrial control fields that require high heat dissipation reliability.
Conclusion
The heat dissipation design of high-power AC/DC power supplies needs to take into account multiple factors such as efficiency, space, and noise. Although niche heat dissipation solutions have a narrow application range, they have irreplaceable advantages in specific scenarios. Microchannel phase change heat dissipation technology accurately overcomes the problem of local high temperatures, the heat pipe-vapor chamber composite system achieves global temperature balance, and nano thermal conductive coatings optimize interface heat conduction efficiency. All three schemes can effectively make up for the shortcomings of traditional popular schemes.
Share our interesting knowledge and stories on social media