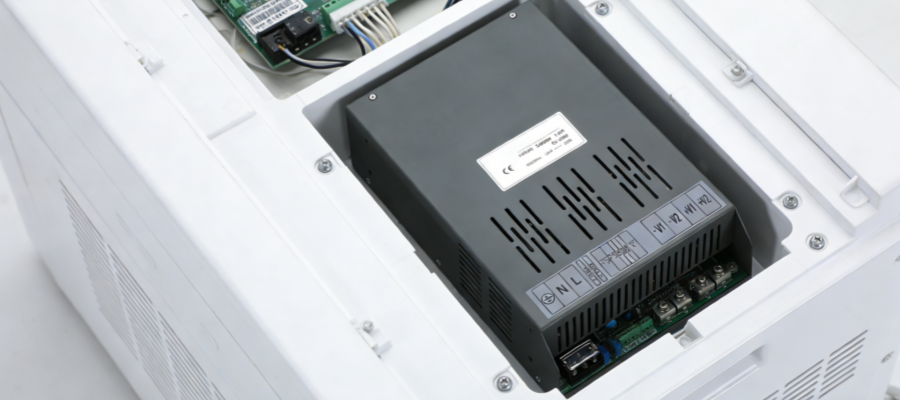
As the "power core" of electronic devices, switching power supplies are widely used in industrial control, consumer electronics, new energy and other fields. If the heat generated during their operation cannot be dissipated in a timely manner, it will directly affect the conversion efficiency and service life, and even cause component damage. Therefore, selecting an appropriate heat dissipation method is a core link to ensure the long-term and reliable operation of switching power supplies.
Switching Power Supply Heat Dissipation Methods and Application Scenarios
1. Natural Convection Cooling
Natural convection cooling relies on the natural processes of heat conduction, convection, and radiation, requiring no additional auxiliary equipment. It is the most basic form of heat dissipation for switching power supplies. By increasing the heat dissipation area and using high-thermal conductivity materials, heat is naturally dissipated from the internal components of the switching power supply into the environment. This method is noiseless, has no risk of mechanical failure, and is inexpensive, making it suitable for low-power switching power supplies below 20W, such as small adapters and smart home control modules. However, its limitations are also quite obvious; the heat dissipation efficiency is greatly affected by ambient temperature, and high-power applications require oversized heat sinks, resulting in bulky equipment.
2. Forced Air Cooling
Forced air cooling uses fans to accelerate airflow, significantly improving convective heat transfer efficiency. It is the mainstream heat dissipation method for 100W-1000W switching power supplies. The application of intelligent speed control technology allows the fan speed to dynamically adjust according to the internal temperature of the switching power supply. At low loads, it runs at a low speed to reduce noise, and at high loads, it speeds up to enhance heat dissipation. This method effectively reduces equipment size and material costs and is widely used in medium-power applications such as server power supplies and industrial control equipment. However, fans have a limited lifespan and require regular maintenance and replacement after long-term use.
3. Hybrid Cooling
Hybrid cooling combines the advantages of natural convection cooling and forced air cooling. At low loads and low ambient temperatures, it relies on natural convection cooling, and in high-load or high-temperature environments, it automatically activates the fan for assistance. This method avoids the lag problem of pure forced air cooling and reduces the wear and tear caused by continuous high-load operation of the fan, extending the overall service life. It is especially suitable for environments with large temperature fluctuations, such as communication equipment rooms and outdoor equipment, allowing the switching power supply to maintain a stable temperature field under different operating conditions.
4. Liquid Cooling
Liquid cooling uses liquid as the heat transfer medium, utilizing its high specific heat capacity to quickly dissipate heat. It is the core heat dissipation solution for high-power switching power supplies above several kilowatts. The heat generated by power devices inside the switching power supply is dissipated through a circulating system, making it suitable for high-heat load scenarios such as new energy vehicle charging stations and large industrial power supplies. Modern liquid cooling technology addresses the risk of leakage through insulation design, while also offering the advantages of low noise and uniform heat dissipation, becoming an important technological direction for high-power density switching power supplies.
Switching Power Supply Heat Dissipation Optimization Principles
The heat dissipation effect of a switching power supply depends not only on the cooling method but also on the structural design and material selection. Reasonable layout of internal components, concentrating high-heat-generating power transistors and transformers near cooling components, shortens the heat transfer path; using high-efficiency heat-conducting materials such as aluminum alloy and copper, combined with thermal interface materials such as thermal grease, reduces contact thermal resistance; integrating temperature monitoring modules enables intelligent control of the heat dissipation strategy. These details can significantly improve heat dissipation efficiency. IDEALPLUSING incorporates diverse technological considerations into the heat dissipation design of its switching power supplies, allowing products to adapt to the temperature requirements of different scenarios.
Heat dissipation design is a key link in the performance optimization of switching power supplies. It is necessary to comprehensively select the appropriate heat dissipation scheme according to power level, application environment and cost budget. With the improvement of power density, heat dissipation technology is constantly innovating, providing a more reliable guarantee for the stable operation of switching power supplies.
IDEALPLUISNG Power Expert:
We focus on the research and development, sales and services in the fields of DC-DC power modules, AC-DC rectifier modules, DC-AC inverters, AC power supplies, DC power supplies, LED power supplies, chargers, rectifier systems, etc., providing personalized, efficient, reliable and cost-effective power solutions for all walks of life.
Thank you for considering our services.