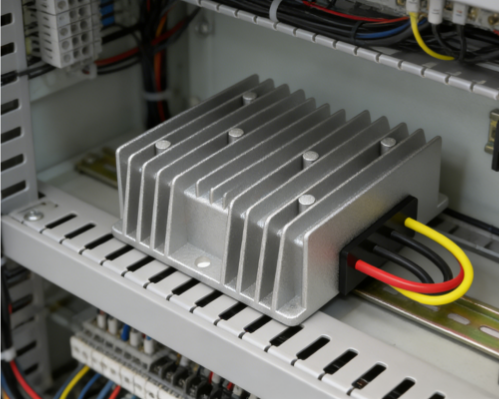
In diverse application scenarios such as industrial power supply, automotive electronics, and energy storage modules, the input voltage of power equipment is often affected by factors such as power supply fluctuations, line losses, and load changes, exhibiting a wide range of variations. This places stringent demands on the voltage adaptation capabilities of DC-DC converters. In the process of achieving wide voltage adaptation, ripple interference becomes an unavoidable technical challenge – excessive ripple can affect the working stability of downstream precision circuits, and even cause signal distortion and reduced device lifespan. How to balance the compatibility of wide voltage input with low ripple output quality is a core issue in the design and application of DC-DC converters, and a direction of continuous exploration in the industry.
The essence of wide voltage adaptation is to enable the DC-DC converter to stably output the target voltage within a preset wide input voltage range, while maintaining conversion efficiency and reliability, through optimization of the core topology structure and adjustment of control strategies. Currently, mainstream wide voltage adaptation designs are mostly based on improvements to classic topologies and the application of new topologies, balancing topology adaptability and control precision.
In terms of topology selection, the BOOST-BUCK (step-up/step-down) topology is one of the core solutions for wide voltage adaptation. Unlike traditional topologies that can only step up or step down the voltage, it can achieve stable voltage regulation when the input voltage is higher than, lower than, or equal to the output voltage, adapting to scenarios such as automotive 12V/24V compatibility and industrial 24V-72V wide voltage input. To improve conversion efficiency under wide voltage conditions, some designs use synchronous rectification technology, replacing traditional diodes with MOS transistors to reduce conduction losses, especially in wide voltage conditions with low input voltage and high current output, effectively reducing energy loss. In addition, isolated topologies such as flyback and forward converters are also widely used in wide voltage adaptation. They not only achieve electrical isolation between input and output, improving safety, but also broaden the voltage adaptation range through optimized transformer winding design, adapting to industrial high-voltage wide-range input scenarios.
At the control strategy level, the hybrid modulation mode of pulse width modulation (PWM) and pulse frequency modulation (PFM) is a key technical means for wide voltage adaptation. PWM mode achieves voltage stabilization and ensures output accuracy by adjusting the duty cycle at a fixed frequency when the input voltage is stable and the load is heavy; PFM mode, on the other hand, adapts to voltage changes by adjusting the pulse frequency when the input voltage fluctuates significantly and the load is light, reducing static power consumption. The hybrid modulation mode allows the converter to maintain high efficiency across the full wide-voltage input and full load range, avoiding the sudden efficiency drop and output instability problems that occur with a single modulation mode under extreme wide-voltage conditions. At the same time, high-precision sampling and feedback circuits are fundamental to wide-voltage adaptation. By real-time sampling of the input and output voltages, combined with closed-loop control algorithms, the modulation parameters are quickly adjusted to counteract the effects of input voltage fluctuations and ensure output voltage stability.
In wide-voltage adaptation scenarios, ripple suppression is far more challenging than in conventional constant-voltage input scenarios. Wide input voltage fluctuations trigger frequent shifts in the converter’s operating mode, which readily causes the superposition of switching noise, inductor current ripples and capacitor charge-discharge ripples. This not only amplifies the output ripple amplitude but also complicates its frequency characteristics. Conventional ripple suppression measures—such as adding filter capacitors and inductors at the output—often fail to deliver satisfactory performance under wide-voltage operating conditions. It is therefore imperative to adopt a multi-dimensional, systematic and advanced suppression strategy from the design stage to realize precise ripple regulation.
From the perspective of hardware circuit optimization, optimizing the selection and layout of power devices is the first step in ripple suppression. The switching speed and on-resistance of power switching transistors (MOSFETs), and the recovery time of diodes, all affect the noise generated during the switching process. In wide-voltage designs, power devices with low switching losses and soft recovery characteristics should be selected to reduce voltage spikes and current oscillations during switching. Furthermore, the rationality of the PCB layout directly affects parasitic parameters. The power circuit of a wide-voltage converter should follow the "short, thick, and close" principle, shortening the connections between power devices, inductors, and capacitors to reduce parasitic inductance and capacitance, and minimize the coupling of switching noise to the output through parasitic parameters. In addition, using a composite filtering structure of "inductor + multiple capacitors" is a core method for ripple suppression under wide-voltage conditions. Unlike single-capacitor filtering, the integration of electrolytic, ceramic and tantalum capacitors enables robust ripple attenuation across the full frequency spectrum—ceramic capacitors mitigating high-frequency ripple, electrolytic counterparts suppressing low-frequency ripple. When paired with common-mode and differential-mode inductors, this hybrid configuration delivers comprehensive ripple suppression over all frequency bands. For the prominent inductor current ripple issue under wide-voltage conditions, inductors may employ low-loss core materials with high saturation magnetic flux density; additionally, optimized winding designs reduce equivalent series resistance, thereby minimizing ripple originating from inductive components.
From the perspective of control algorithm optimization, precise ripple compensation and suppression strategies can effectively reduce ripple variations caused by wide voltage fluctuations. In closed-loop control, introducing feedforward control algorithms is an important advanced technique – by real-time detection of the input voltage, the PWM/PFM modulation parameters are adjusted in advance to counteract the impact of input voltage fluctuations on the output voltage, reducing the amplitude variation of the output ripple. For example, when the input voltage suddenly increases, feedforward control can quickly reduce the duty cycle to avoid ripple spikes caused by a sudden increase in output voltage; when the input voltage suddenly drops, the duty cycle is quickly increased to prevent the output voltage from dropping. Simultaneously, using digital control technology instead of traditional analog control enables more precise ripple suppression. Digital control can implement complex control algorithms through programming, such as self-tuning of PID parameters, adjusting PID parameters in real time based on changes in input voltage and load fluctuations, ensuring the converter always maintains optimal control accuracy and reducing ripple overshoot and oscillation; it can also incorporate ripple prediction algorithms, analyzing historical ripple data to predict ripple trends in advance and perform active compensation, further reducing output ripple.
From the perspective of soft-switching technology application, soft switching can effectively reduce switching noise under wide voltage conditions, reducing ripple generation at the source. Traditional hard-switching technology results in simultaneous voltage and current presence at the switching tube’s turn-on and turn-off instants, generating substantial switching losses and electromagnetic interference (EMI) that convert to ripple and degrade output performance. By contrast, soft-switching technologies—including zero-voltage switching (ZVS) and zero-current switching (ZCS)—eliminate this voltage-current overlap: ZVS reduces the switching transistor’s voltage to zero prior to turn-on, while ZCS drops its current to zero before turn-off.This significantly reduces switching losses and EMI noise. In wide-voltage DC-DC converters, combining soft-switching technology with buck-boost topologies effectively suppresses ripple generated during the switching process, especially under high input voltage and high switching frequency conditions. The ripple suppression effect of soft-switching technology is even more significant in these wide-voltage scenarios, while also improving the converter's conversion efficiency, achieving a dual optimization of efficiency and ripple.
In practical applications, wide-voltage adaptation and ripple suppression are not isolated technical aspects, but rather an interconnected and interdependent whole, requiring customized solutions based on specific application scenarios.High ripple requirements (typically requiring output ripple less than 100mV) necessitate the use of a BOOST-BUCK buck-boost topology, combined with a hybrid modulation mode, a composite filtering structure at the output, and the inclusion of feedforward control and soft-switching technology to balance the stability of wide-voltage adaptation and the effectiveness of ripple suppression. In industrial micro-power supply scenarios, the input voltage is 24V-72V, and the load is a low-power precision sensor with extremely high ripple requirements (output ripple needs to be less than 50mV). In this case, an isolated flyback topology can be used, combined with a digitally controlled PID self-tuning algorithm, optimizing the parameters of the filtering circuit, and paying attention to PCB electromagnetic shielding design to reduce external interference and the superposition of internal ripple.
Furthermore, the effectiveness of wide-voltage adaptation and ripple suppression is closely related to component selection and manufacturing process control. In component selection, high-precision and high-stability components should be used, such as low-temperature drift sampling resistors, high-voltage capacitors, and low-noise operational amplifiers, to avoid performance deviations of the components themselves affecting wide-voltage adaptation and ripple suppression. In the manufacturing process, strict control of PCB processing accuracy and component welding quality is essential to reduce parasitic parameters and contact resistance caused by process issues, ensuring that the performance of the circuit design is fully realized. With the rapid development of industries such as industrial intelligence, new energy vehicles, and energy storage, the demands on DC-DC converters from power equipment are becoming increasingly diverse. The range of wide-voltage adaptation is continuously expanding, and the precision requirements for ripple suppression are constantly increasing. At the same time, converters are also required to be miniaturized, highly integrated, and low-power. In the future, the technological development of wide-voltage adaptation and ripple suppression will move towards "topology innovation + digital intelligence + new material applications."
In terms of topology innovation, new three-level and multi-level topologies will gradually be applied to wide-voltage DC-DC converters. By segmenting the voltage levels, the voltage stress on individual power devices is reduced, improving wide-voltage adaptation capabilities while reducing switching noise and ripple generation. In terms of digital intelligence, technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning will be deeply integrated with converter control, achieving adaptive wide-voltage adaptation and ripple suppression. By learning from operating data under different working conditions, the topology parameters and control strategies will be automatically optimized, enabling efficient adaptation and low-ripple output in all scenarios without manual intervention. In terms of new material applications, the popularization of wide-bandgap semiconductor materials such as gallium nitride (GaN) and silicon carbide (SiC) will significantly improve the performance of power devices. Their high switching speed, high voltage resistance, and low loss characteristics will allow converters to maintain efficient operation over a wider voltage range while reducing switching noise, providing a hardware foundation for ripple suppression.
The realization of wide-voltage adaptation is the basis for DC-DC converters to adapt to complex application scenarios, while ripple suppression is crucial for ensuring the stable operation of downstream equipment. The technological integration and advancement of both aspects not only test the skills of circuit design but also require the accumulation of technology in topology, control, devices, and processes. Against the backdrop of continuous technological iteration, balancing the compatibility of wide-voltage adaptation, the precision of ripple suppression, and the overall performance of the converter will become the core direction of DC-DC converter technology development, providing more stable and efficient solutions for power supply systems in various industries.
We at IDEALPLUSING not only provide products, but also strive to provide customers with suitable power supply solutions and quotations.
Our core competitiveness lies in carefully selecting a variety of power supply options to help customers evaluate and choose the most suitable power supply solution.
We can offer AC DC power supply, DC AC inverter, AC AC power source(single phase or 3 phases),AC DC Ground Power Unit...
Share our interesting knowledge and stories on social media