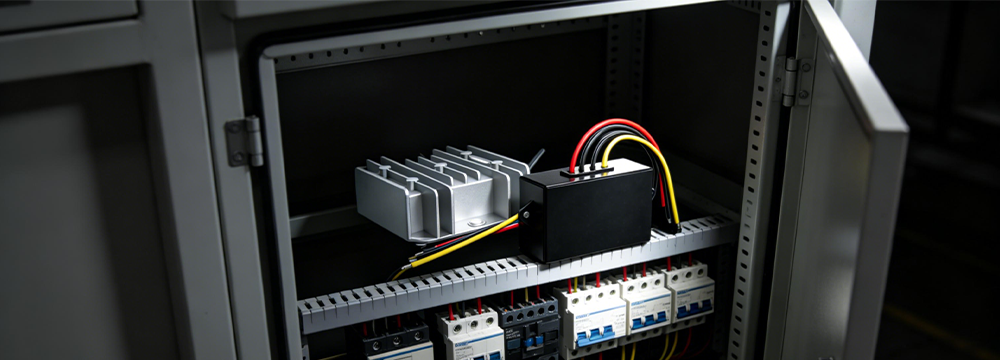
DC-DC converters serve as core power conversion components in industrial automation, new energy and other applications. Yet the harsh conditions of industrial settings—including high ambient temperatures, sealed enclosures and high-load operation—combined with inherent device power loss, can easily trigger overheating and performance malfunctions. It is therefore critical to design targeted, effective heat dissipation solutions aligned with the unique characteristics of industrial environments to ensure consistent equipment operation. This paper briefly outlines the core heat dissipation strategies and practical measures for industrial DC-DC converters.
I. Core Premise: Precise Loss Control and Clear Requirements
The essence of heat dissipation is to dissipate power loss. In industrial settings, converters operate under high loads for extended periods, resulting in significant power loss. It is necessary to first calculate the power loss using the converter's datasheet efficiency curve and actual load, then determine the maximum allowable junction temperature of the device based on the ambient temperature and installation space, calculate the heat dissipation requirements, and reserve sufficient redundancy to cope with extreme environmental fluctuations.
II. Basic Measures: Low-Cost and Efficient Heat Dissipation
In low-to-medium power and moderate temperature environments, optimizing component selection, layout, and installation can meet the requirements most cost-effectively.
(I) Component Selection: Reducing Loss at the Source
Prioritize converters with conversion efficiency ≥90% to reduce losses; select power devices and integrated modules with heat dissipation pads, and use low-loss inductors and capacitors to reduce heat generation at the source.
(II) PCB Layout: Optimizing Heat Conduction
Increase the copper foil area for heat dissipation of power devices, use copper foil with a thickness of 2oz or more and maintain continuity; separate power devices from heat-sensitive components to avoid heat accumulation; design evenly distributed thermal vias to conduct heat from the surface to the inner layers, improving heat conduction efficiency.
(III) Installation Method: Leveraging the Environment
Prioritize natural convection cooling, placing the converter near ventilation openings and away from high-temperature components; avoid obstructing the heat dissipation surface, and leave 5-10mm of space for heat dissipation to prevent dust accumulation and blockage of cooling channels.
III. Advanced Solutions: Addressing Demanding Scenarios
In high-power, high-temperature or enclosed spaces, enhanced thermal dissipation is a must. Heat dissipation can be boosted via passive cooling—using thermally conductive aluminium/copper or applying professional thermal paste on contact surfaces to optimize heat transfer. So too can active cooling be achieved: fans and similar devices generate airflow to lower temperatures. These methods markedly improve heat dissipation and ensure the converter’s stable operation. Critical as the converter is, its thermal management is equally vital; it demands a suitable working environment, making an efficient heat dissipation solution indispensable.
The thermal design of industrial DC-DC converters requires precise loss calculations as a basis, followed by step-by-step optimization considering environmental characteristics. For low-to-medium power applications, cost-effective temperature control can be achieved through component selection, PCB layout, and natural convection cooling; however, high-power, high-temperature, or enclosed environments require enhanced measures such as thermal interface materials, heat sinks, and active forced-air cooling. A systematic thermal management solution effectively ensures the long-term stable operation of the converter in harsh industrial environments, improving overall equipment reliability.
We at IDEALPLUSING not only provide products, but also strive to provide customers with suitable power supply solutions and quotations.
Our core competitiveness lies in carefully selecting a variety of power supply options to help customers evaluate and choose the most suitable power supply solution.
We can offer AC DC power supply, DC AC inverter, AC AC power source(single phase or 3 phases),AC DC Ground Power Unit...
Share our interesting knowledge and stories on social media