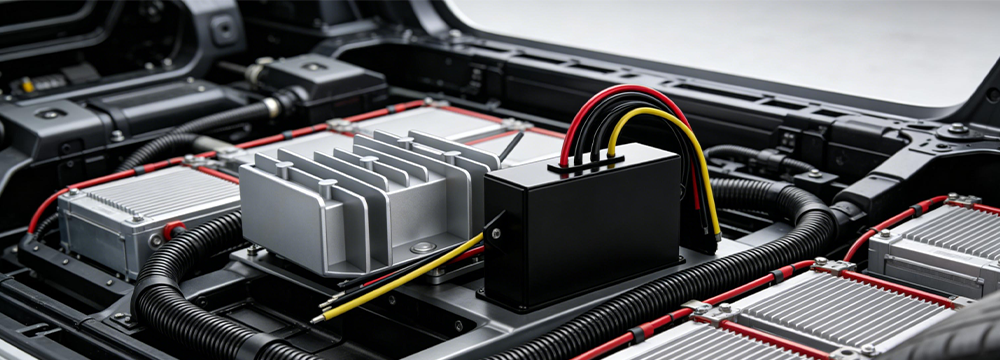
As a core component of the automotive power system, the DC-DC converter performs a critical function, converting the high-voltage DC power from the vehicle battery into the low-voltage DC power required by all on-board electrical appliances and control systems. Unlike industrial and consumer electronics, the automotive operating environment presents significant challenges: strong electromagnetic interference, wide temperature fluctuations, frequent mechanical vibrations, and severe voltage transients. These adverse conditions can easily lead to increased output voltage ripple and reduced conversion efficiency, and in extreme cases, may even cause equipment failure or sudden shutdown, directly affecting the normal operation of on-board electrical equipment and overall vehicle safety.
1. Main Interference Sources in Automotive DC-DC Converter Applications
To boost the anti-interference ability of automotive DC-DC converters, the first thing you need to do is figure out the main sources of interference in vehicle settings and take targeted steps to fix them. Interference in car applications mainly falls into two kinds: electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electromagnetic susceptibility (EMS). EMI can be broken down even further into conducted interference and radiated interference. The former mostly comes from voltage fluctuations in the car’s power battery, start-stop surges from the starter motor, coupling interference from high-voltage wiring harnesses, and switching noise from other on-board electrical devices. Such interference is transmitted to the DC-DC converter via power lines and signal lines. Radiated interference, by contrast, originates from the electromagnetic radiation of vehicle radar, wireless communication modules and high-voltage wiring harnesses, as well as the impact of the external electromagnetic environment. This type of interference couples into the converter’s internal circuits through spatial radiation propagation. In addition, temperature fluctuations (-40℃ to 125℃) and severe vibrations in automotive applications can lead to parameter drift and poor contact of internal components of the converter, indirectly reducing its anti-interference performance. These are all interference factors that need to be carefully considered during the design process.
2. Hardware Circuit Optimization: Foundation of Anti-Interference Design
Optimizing the hardware circuit design is the foundation and the most crucial technical means for improving the anti-interference capability of automotive DC-DC converters. In the power input circuit design, an EMI filtering circuit needs to be added, using a combination of common-mode inductors and X/Y capacitors to suppress conducted interference at the input and output. Common-mode inductors effectively suppress common-mode interference signals, X capacitors filter differential-mode interference between power lines, and Y capacitors suppress common-mode interference to ground. The filtering component parameters must be carefully selected to ensure the filtering frequency covers the main interference frequency band in vehicles (10kHz~1GHz). In the power conversion circuit, low on-resistance and fast switching speed MOSFETs should be used to reduce electromagnetic noise generated during switching; the PCB layout should be optimized to shorten the wiring length of the power circuit, reduce parasitic inductance, and avoid radiation interference caused by inductive coupling. Power devices and control circuits should be separated to prevent interference from the power circuit affecting the stability of the control circuit.
3. Shielding Protection Design: Blocking Radiation and Conduction Interference
Robust shielding protection design can effectively block radiated interference and mitigate the impact of external disturbances on a converter’s internal circuitry. For automotive DC-DC converters, the enclosure shall be fabricated from a highly conductive metal material—aluminum alloy or stainless steel, for instance. Proper grounding of this metal casing is a must, as it forms a complete electromagnetic shielding barrier: not only does it block external radiated interference from penetrating the converter, but it also suppresses electromagnetic radiation emitted by the converter itself. For sensitive internal components, including control chips, feedback resistors and sampling circuits, individual metal shielding covers are to be fitted; this safeguards them from interference stemming from the power circuit and external radiation alike. As for automotive wiring harnesses, shielded types should be adopted, with meticulous planning of wiring layouts. High-voltage and low-voltage signal lines must be segregated to prevent interference coupling from high-voltage lines to low-voltage signal paths, and both ends of each harness should be grounded properly to reduce conductive interference.
4. Software Control Strategy Optimization: Supplementing Hardware Deficiencies
To compensate for shortcomings in hardware design and further boost anti-interference performance, optimizing software control strategies is a pivotal supplement. First and foremost, the control chip of an automotive DC-DC converter should be a model with superior anti-interference capability, boasting wide voltage input range and stable operation under high-temperature conditions. In the design of control algorithms, advanced methodologies such as adaptive PID control and sliding mode control shall be incorporated. This elevates the converter’s response speed to input voltage transients and load variations, curtails output voltage fluctuations, and enhances overall system robustness. Also to be added is interference suppression logic, which filters sampled voltage and current signals: it eliminates spurious interference signals and prevents the control chip from making misjudgments or triggering false actions due to external disturbances. Beyond this, protective mechanisms for overvoltage, overcurrent, overheating and undervoltage can be configured. Should the converter encounter abnormal operating conditions caused by severe interference, these protection functions will be activated promptly—this not only prevents converter damage but also facilitates subsequent fault diagnosis and troubleshooting.
5. Production Process Improvement and Practical Verification
Ensuring the effectiveness of anti-interference design hinges on two crucial steps: upgrading production processes and conducting practical verification tests. During the production phase, electronic components with high precision, high stability, temperature drift resistance and vibration resistance are to be selected. Welding quality, too, must be strictly controlled; this avoids poor contact arising from cold solders or incomplete welds, which would otherwise compromise anti-interference performance. The converter is then subjected to rigorous environmental adaptability testing, where vehicle operating scenarios—such as high and low temperatures, mechanical vibration and voltage transients—are simulated. These tests verify whether the converter’s anti-interference capability meets pre-set design criteria. Concurrently, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing is performed, which detects and quantifies both the electromagnetic radiation emitted by the converter and its susceptibility to external electromagnetic interference. Based on the problems found during testing, hardware design and shielding measures are optimized to ensure that the converter meets automotive EMC standards.
In summary, improving the interference resistance of DC-DC converters in vehicle scenarios is a systematic engineering project that requires collaborative efforts from multiple aspects, including hardware circuit optimization, shielding design, software control upgrades, production process control, and practical verification, considering the interference characteristics of vehicle environments. As automotive electronic systems become increasingly complex, the requirements for the interference resistance of DC-DC converters will continue to rise. In the future, it will be necessary to further integrate new filtering technologies and intelligent control algorithms to drive the development of converters towards high interference resistance, high stability, and high efficiency, providing strong support for the safe and reliable operation of new energy vehicles.
We at IDEALPLUSING not only provide products, but also strive to provide customers with suitable power supply solutions and quotations.
Our core competitiveness lies in carefully selecting a variety of power supply options to help customers evaluate and choose the most suitable power supply solution.
We can offer AC DC power supply, DC AC inverter, AC AC power source(single phase or 3 phases),AC DC Ground Power Unit...